Choking
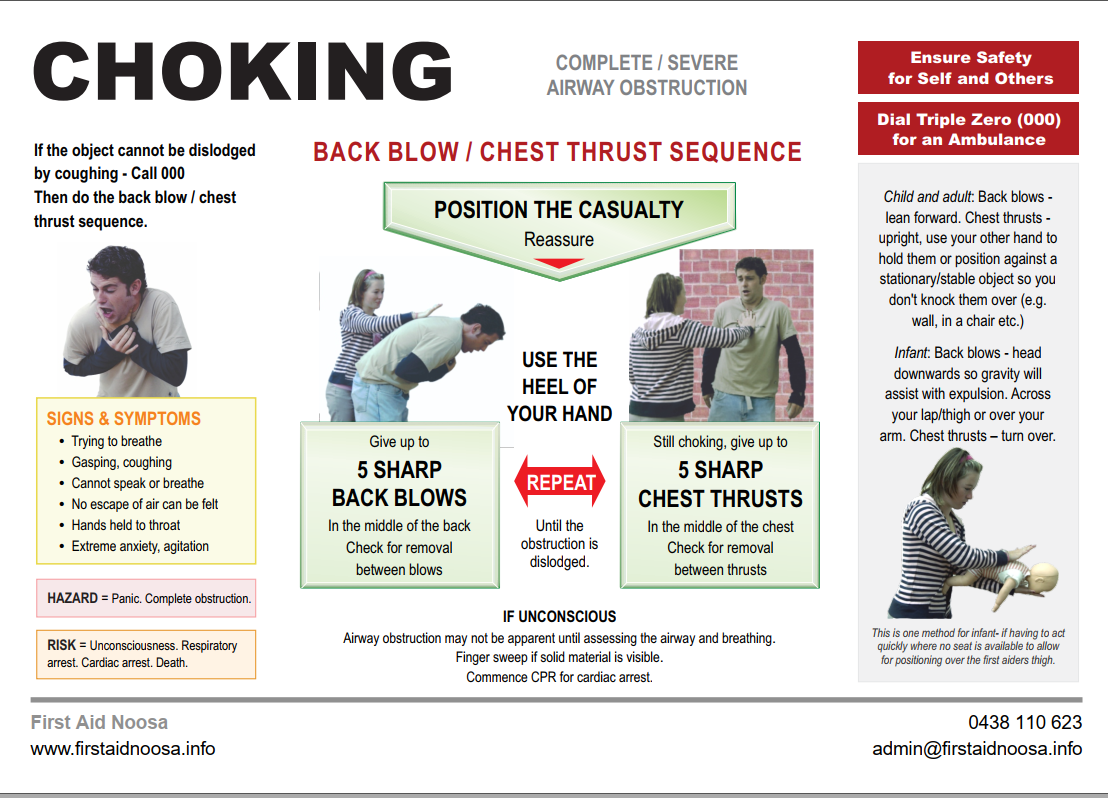
Choking is the result of the lodgement of a foreign object in the casualty’s airway. In some instances, the object lodges at the entry to the airway (partial obstruction), but does not enter the airway itself. This will cause the casualty to start coughing which is the body’s way of trying to expel the object out.
If the object is firmly lodged in the airway (complete obstruction), coughing at least keeps it high in the windpipe, though it will not necessarily expel it.
Signs and symptoms
Persistent cough
Inability to breathe, speak, cry or cough
Clutching at the throat
Anxiety, restlessness
Collapse and unconsciousness
First aid
If partial blockage – encourage the casualty to keep coughing
If complete blockage – call for medical assistance urgently
Position the casualty – adults on their side, children heads lower than their body
Deliver up to five sharp back blows between the shoulder blades, and clear any obstructions that may have come out.
If back blows are unsuccessful perform five chest thrusts ( the same as if delivering CPR chest compressions).
If the casualty has stopped breathing commence CPR